tuple Conversion FunctionTBA
create an empty list
for each line in the file:
append the line to the empty list
file = open('numbs.txt', 'r')
numbers = []
for line in file:
numbers.append(int(line))
total = 0
for num in numbers:
total += num
average = round(total/len(numbers))
above_average = 0
for num in numbers:
if num > average:
above_average += 1
print(above_average)
lenfor loops
for loop
file = open('numbs.txt', 'r')
total = 0
numbers = []
for line in file:
num = int(line)
numbers.append(num)
total += num
average = round(total/len(numbers))
above_average = 0
for num in numbers:
if num > average:
above_average += 1
print(above_average)
len on the list objectmax functionmin to get the minimum value>>> number_1 = 5 >>> number_2 = number_1 >>> number_2 5
>>> number_1 = 6 >>> number_1 6 >>> number_2 5
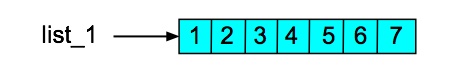
>>> list_1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] >>> list_1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
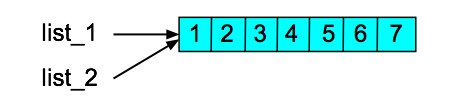
>>> list_2 = list_1 >>> list_2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
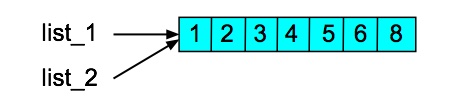
>>> list_1[6] = 8 >>> list_1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8] >>> list_2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8]
>>> list_1[6] = 8
>>> list_1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
>>> list_2 = [] + list_1
>>> list_2
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
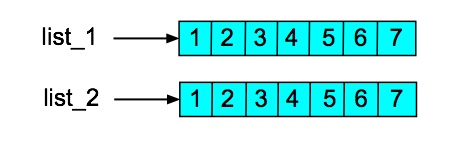
>>> list_1[6] = 8 >>> list_1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8] >>> list_2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
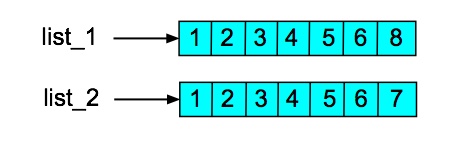
>>> list_1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
>>> list_2 = list_1[:]
>>> list_1[6] = 10
>>> list_1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10]
>>> list_2
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
use the filename to create a file object
create an empty list
for each line in the file:
convert the line into a number
add the number to the empty list
return a variable pointing to the list
#! /usr/bin/python3
# reads a text file containing integers
# and prints it
# reads a text file of integers
# and stores them in a list which is returned
def read_integers_into_list(filename):
file = open(filename, "r")
new_list = []
for line in file:
number = int(line)
new_list.append(number)
file.close()
return new_list
number_list = read_integers_into_list("temperatures.txt")
print("List:", number_list)
set an accumulator to zero
loop through the list using the list address:
add each number to the accumulator
return the accumulator divided by the length of the list
def average_list(list):
total = 0
for index in range(len(list)):
total += list[index]
return total/len(list)
>>> def double_list(list): ... for index in range(len(list)): ... list[index] = 2 * list[index] ... >>> numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] >>> double_list(numbers) >>> numbers [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
>>> list_1 = [1 , 2.5, True, "foo"] >>> for index in range(len(list_1)): ... print(list_1[index], type(list_1[index])) ... 1 <class 'int'> 2.5 <class 'float'> True <class 'bool'> foo <class 'str'>
>>> list_2 = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6, 7,]] >>> for index in range(len(list_2)): ... print(list_2[index], type(list_2[index])) ... 1 <class 'int'> 2 <class 'int'> 3 <class 'int'> 4 <class 'int'> [5, 6, 7] <class 'list'>
>>> two_d_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]] >>> two_d_list [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
>>> for element in two_d_list: ... print(element) ... [1, 2, 3] [4, 5, 6] [7, 8, 9]
>>> two_d_list[0] [1, 2, 3] >>> two_d_list[1] [4, 5, 6] >>> two_d_list[2] [7, 8, 9]
>>> two_d_list[0][0] 1 >>> two_d_list[0][1] 2 >>> two_d_list[0][2] 3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
for row in range(len(two_d_list)): ... for column in range(len(two_d_list[row])): ... print(two_d_list[row][column], end=" ") ... print() ... 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
print to start a new line2017-06-01 67 2017-06-02 71 2017-06-03 69 ...
create an empty list
for each line in the file:
turn the line into a list using split
convert the temperature into an integer
add this new list to the two-dimensional list
entries = []
for line in file:
entry = line.split()
entry[1] = int(entry[1])
entries.append(entry)
set a variable for the index of the entry with the highest temperature to 0
set a variable for the highest temperature to a low value
for each index in the two-dimensional list:
get the temperature for that date
if the temperature is greater than the highest temperature:
set the highest temperature to the current temperature
set the highest index to the current index
return the date of the entry with the highest index
def higest_temp_date(entries):
highest_index = 0
max_temp = -500
for index in range(len(entries)):
temp = entries[index][1]
if temp > max_temp:
max_temp = temp
highest_index = index
return entries[highest_index][0]
>>> tuple_1 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) >>> tuple_1 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
>>> tuple_2 = (1, 2.5, False, "Sam") >>> tuple_2 (1, 2.5, False, 'Sam')
>>> tuple_1[0] 1
for loop to print all the elements
>>> for number in tuple_1: ... print(number) ... 1 2 3 4 5
>>> tuple_3 = tuple_1 + tuple_2 >>> tuple_3 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2.5, False, 'Sam')
>>> tuple_4 = tuple_1 * 3 >>> tuple_4 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
in operator
>>> "Sam" in tuple_2 True
len function works with tuples
>>> tuple_1 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) >>> len(tuple_1) 5
min
>>> min(tuple_1) 1
max
>>> max(tuple_1) 5
index method
>>> tuple_1.index(3) 2
>>> tuple_1 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) >>> tuple_1[1:3] (2, 3) >>> tuple_1[:3] (1, 2, 3) >>> tuple_1[1:] (2, 3, 4, 5) >>> tuple_1[:] (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
>>> tuple_5 = (1)
>>> tuple_5 1
type function
type(tuple_5) <class 'int'>
>>> tuple_5 = (1,) >>> tuple_5 (1,) >>> type(tuple_5) <class 'tuple'> >>> tuple_5[0] 1
>>> empty_tuple = () >>> empty_tuple ()
>>> type(empty_tuple) <class 'tuple'>
tuple Conversion Functiontuple
>>> name = 'Glenn'
>>> tuple(name)
('G', 'l', 'e', 'n', 'n')
>>> digits = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] >>> tuple(digits) (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0)
>>> tuple(1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'int' object is not iterable
>>> tuple(True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable
for loop
board = [["O", "X", "X"], ["X", "0", "O"], ["X", "0", "O"]]
>>> for row in range(len(game)): ... for column in range(len(game[row])): ... print(game[row][column], end=" ") ... print() ... O X X X 0 O X 0 O
board = [[' ', ' ', ' '],[' ', ' ', ' '],[' ', ' ', ' ']]
>>> board = [[' ', ' ', ' '],[' ', ' ', ' '],[' ', ' ', ' ']] >>> for row in board: ... print(row) ... [' ', ' ', ' '] [' ', ' ', ' '] [' ', ' ', ' ']
| | ----- | | ----- | |
def print_row(row):
print(row[0] + '|' + row[1] + '|' + row[2])
| |
def print_board():
print_row(board[0])
print('-----')
print_row(board[1])
print('-----')
print_row(board[2])
| | ----- | | ----- | |
while looptry/except statement
GOOD_VALUES = [1,2,3]
def user_move():
while True:
reply = input('Next move (row col): ')
fields = reply.split()
if len(fields) < 2:
print('Need a row number and a column number')
continue
row, col = fields
try:
row = int(row)
col = int(col)
except:
print(row, 'or', col, 'is not a number')
continue
if row not in GOOD_VALUES or col not in GOOD_VALUES:
print('Row and column values must be 1, 2, or 3')
continue
return row, col
prev_moves = []
def user_move():
while True:
reply = input('Next move (row col): ')
fields = reply.split()
if len(fields) < 2:
print('Need a row number and a column number')
continue
row, col = fields
try:
row = int(row)
col = int(col)
except:
print(row, 'or', col, 'is not a number')
continue
if row not in GOOD_VALUES or col not in GOOD_VALUES:
print('Row and column values must be 1, 2, or 3')
continue
if (row, col) in prev_moves:
print(row, col, 'is already taken')
continue
else:
prev_moves.append((row, col))
return row, col
def mark_square(row, col, mark):
board[row - 1][col - 1] = mark
USER_MARK = 'X' MACHINE_MARK = 'O'
while loop to run the game
print_board()
print()
while True:
row, col = user_move()
mark_square(row, col, USER_MARK)
print_board()
print()
while loop
def machine_move():
while True:
row = random.randint(1,3)
col = random.randint(1,3)
if (row, col) not in prev_moves:
prev_moves.append((row, col))
return row, col
else:
continue
print_board()
print()
while True:
row, col = user_move()
mark_square(row, col, USER_MARK)
print_board()
print()
row, col = machine_move()
mark_square(row, col, MACHINE_MARK)
print_board()
print()
for loop to check the rows and columnsif statements for the diagonals
def cell_match(row, col, mark):
return board[row][col] == mark
for loop checks three squares
def game_over(mark):
# check rows
for row in [0,1,2]:
for col in [0,1,2]:
if not cell_match(row, col, mark):
break
if cell_match(row, 0, mark) and cell_match(row, 1, mark) and cell_match(row, 2, mark):
print(mark , 'wins!')
return True
# check columns
for col in [0,1,2]:
for row in [0,1,2]:
cell_mark = board[row][col]
if not cell_match(row, col, mark):
break
if cell_match(0, col, mark) and cell_match(1, col, mark) and cell_match(2, col, mark):
print(mark , 'wins!')
return True
# check diagonals
if cell_match(0, 0, mark) and cell_match(1, 1, mark) and cell_match(2, 2, mark):
print(mark , 'wins!')
return True
if cell_match(0, 2, mark) and cell_match(1, 1, mark) and cell_match(2, 0, mark):
print(mark , 'wins!')
return True
return False
print_board()
print()
while True:
row, col = user_move()
mark_square(row, col, USER_MARK)
print_board()
if game_over(USER_MARK):
break
print()
row, col = machine_move()
mark_square(row, col, MACHINE_MARK)
print_board()
if game_over(MACHINE_MARK):
break
print()